secure-keys
Secure Key Generator for iOS Projects
A utility to securely generate and manage keys for iOS projects using xcframework. This tool helps to safely store and retrieve sensitive keys such as API tokens and access credentials in your iOS app, with support for both local and CI environments.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure that your development environment meets the following prerequisites:
- Ruby 3.3.6 or higher
- iOS 13.0 or higher
Installation
There are multiple ways to install the SecureKeys utility:
Option 1: Install via Homebrew
You can install the SecureKeys utility using Homebrew with the following commands:
brew tap derian-cordoba/secure-keys
brew install derian-cordoba/secure-keys/secure-keys
For more details, you can visit the homebrew-secure-keys repository.
Option 2: Install via RubyGems
Alternatively, you can install the utility using RubyGems:
gem install secure-keys
Option 3: Install via Bundler
If you’re using Bundler to manage your Ruby dependencies, add the gem to your Gemfile:
gem 'secure-keys'
Then, run:
bundle install
For more details, you can visit the homebrew-secure-keys repository.
Usage
Step 1: Define Your Keys
First, determine the keys you want to use in your iOS project. The keys can be sourced either from your Keychain or environment variables. The source of keys is determined by the CI environment variable.
- If
CI=true, keys will be read from environment variables. - If
CI=falseor not set, keys will be read from the Keychain.
You can configure your keys as follows:
From Keychain
- Define the secure-keys record in your Keychain with the key names and values. The value should be a comma-separated list of keys.
security add-generic-password -a "secure-keys" -s "secure-keys" -w "githubToken,apiKey"
If you need to use a custom Keychain identifier, set the SECURE_KEYS_IDENTIFIER environment variable:
export SECURE_KEYS_IDENTIFIER="your-keychain-identifier"
security add-generic-password -a "$SECURE_KEYS_IDENTIFIER" -s "$SECURE_KEYS_IDENTIFIER" -w "githubToken,apiKey"
- Add new keys to the Keychain as needed:
security add-generic-password -a "secure-keys" -s "apiKey" -w "your-api-key"
Or with a custom Keychain identifier:
security add-generic-password -a "$SECURE_KEYS_IDENTIFIER" -s "apiKey" -w "your-api-key"
From Environment Variables
You can define the keys in the .env file or export the keys as environment variables.
export SECURE_KEYS_IDENTIFIER="github-token,api_key,firebaseToken"
export GITHUB_TOKEN="your-github-token"
export API_KEY="your-api-key"
export FIREBASETOKEN="your-firebase-token"
Important: Key names should be formatted in uppercase with
-replaced by_(e.g.,github-tokenbecomesGITHUB_TOKEN).
Custom Delimiter
If you prefer a delimiter other than the default comma, you can set a custom delimiter using the SECURE_KEYS_DELIMITER environment variable:
export SECURE_KEYS_DELIMITER="|"
export SECURE_KEYS_IDENTIFIER="github-token|api_key|firebaseToken"
Step 2: Generate the SecureKeys.xcframework
After configuring your keys, generate the SecureKeys.xcframework by running the following command in your iOS project root directory:
secure-keys
Using Bundler:
bundle exec secure-keys
To get more information about the command, you can use the --help option.
secure-keys --help
# Output
Usage: secure-keys [--options]
-h, --help Use the provided commands to select the params
--ci Enable CI mode (default: false)
-d, --delimiter DELIMITER The delimiter to use for the key access (default: ",")
--[no-]generate Generate the SecureKeys.xcframework
-i, --identifier IDENTIFIER The identifier to use for the key access (default: "secure-keys")
--verbose Enable verbose mode (default: false)
-v, --version Show the secure-keys version
--xcframework Add the xcframework to the target
To avoid defining the SECURE_KEYS_IDENTIFIER and SECURE_KEYS_DELIMITER env variables, you can use the --identifier and --delimiter options.
secure-keys --identifier "your-keychain-or-env-variable-identifier" --delimiter "|"
Also, you can use the short options:
secure-keys -i "your-keychain-or-env-variable-identifier" -d "|"
Step 3: Integrate SecureKeys.xcframework into Your iOS Project
Automatically
[!IMPORTANT] You can see more information about the command using the
--helpoption.
secure-keys --xcframework --help
# Output
Usage: secure-keys --xcframework [--options]
-h, --help Use the provided commands to select the params
--[no-]add Add the SecureKeys XCFramework to the Xcode project (default: true)
-t, --target TARGET The target to add the xcframework
-r, --replace Replace the existing xcframework in the Xcode project (default: false)
-x, --xcodeproj XCODEPROJ The Xcode project path (default: the first found Xcode project)
From the secure-keys command, you can use the --xcframework option to add the SecureKeys.xcframework to the iOS project.
secure-keys --xcframework --target "YourTargetName" --add
If you want to add the SecureKeys.xcframework to an iOS that already contains the SecureKeys source code, you can use the --replace option.
secure-keys --xcframework --target "YourTargetName" --replace
[!IMPORTANT] If you don’t need to generate the
SecureKeys.xcframeworkevery time, you can use the--no-generateoption.
secure-keys --no-generate --xcframework --target "YourTargetName"
Also, you can specify your Xcode project path using the --xcodeproj option.
secure-keys --xcframework --target "YourTargetName" --xcodeproj "/path/to/your/project.xcodeproj"
[!IMPORTANT] By default, the xcodeproj path would be the first found Xcode project.
If you don’t want to use the CLI options, you can configure some env variable to interact with the secure-keys command.
# e.g (Large version)
export SECURE_KEYS_XCFRAMEWORK_TARGET="YourTargetName"
export SECURE_KEYS_XCFRAMEWORK_ADD=true
export SECURE_KEYS_XCFRAMEWORK_REPLACE=true
export SECURE_KEYS_XCFRAMEWORK_XCODEPROJ="/path/to/your/project.xcodeproj"
# e.g (Short version)
export XCFRAMEWORK_TARGET="YourTargetName"
export XCFRAMEWORK_ADD=true
export XCFRAMEWORK_REPLACE=true
export XCFRAMEWORK_XCODEPROJ="/path/to/your/project.xcodeproj"
# Run the command
secure-keys --xcframework
Manually
- From the iOS project, click on the project target, select the
Generaltab, and scroll down to theFrameworks, Libraries, and Embedded Contentsection.
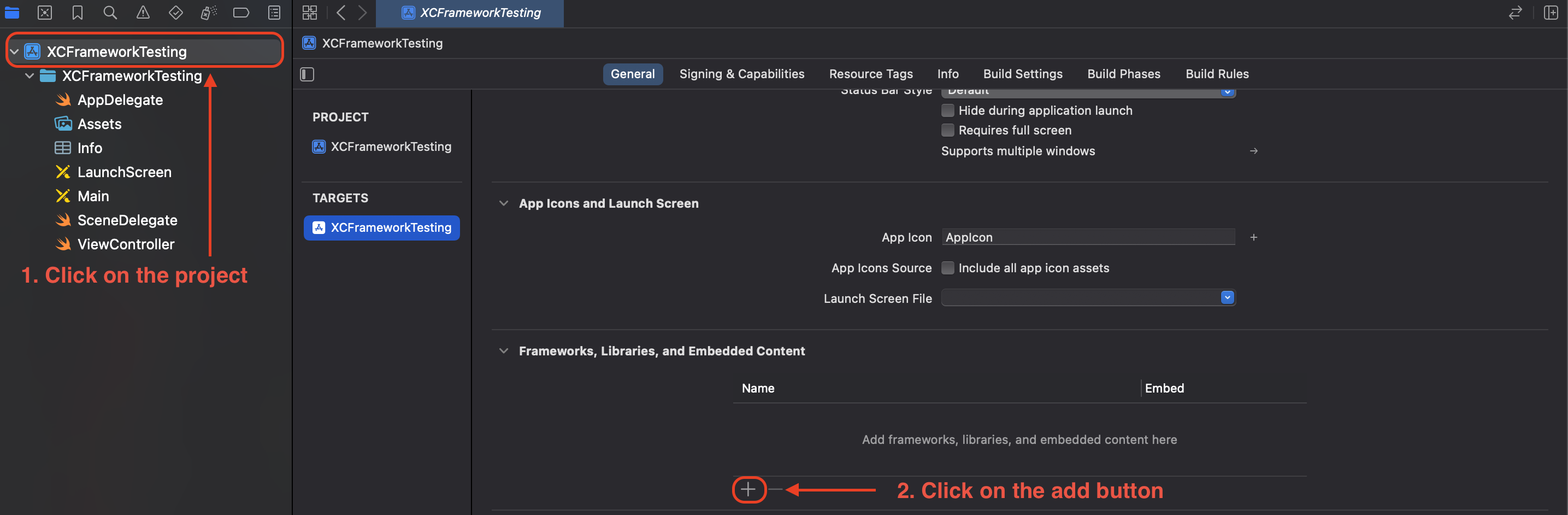
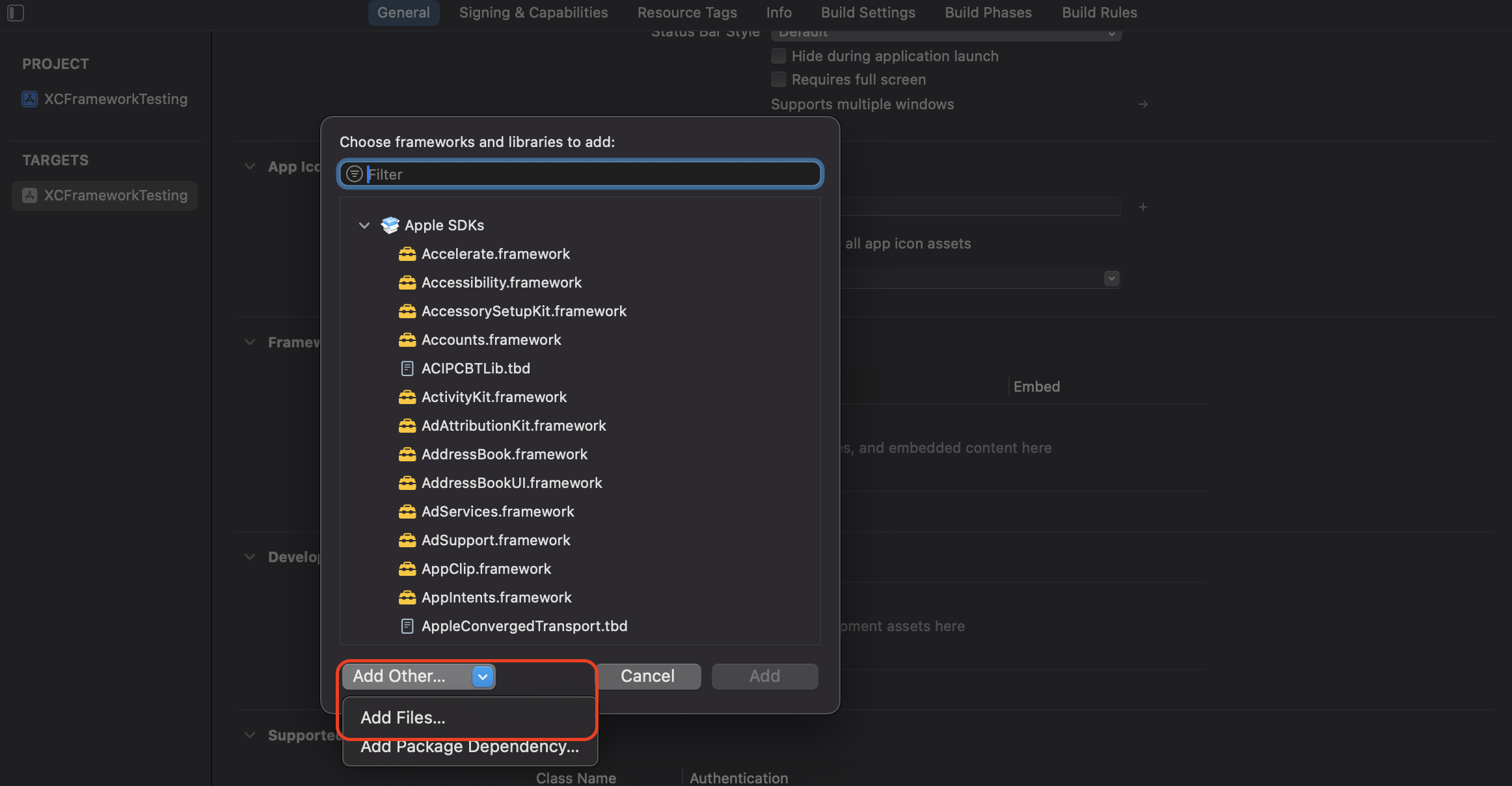
- Click on the
Add Other...button and click on theAdd Files...option.
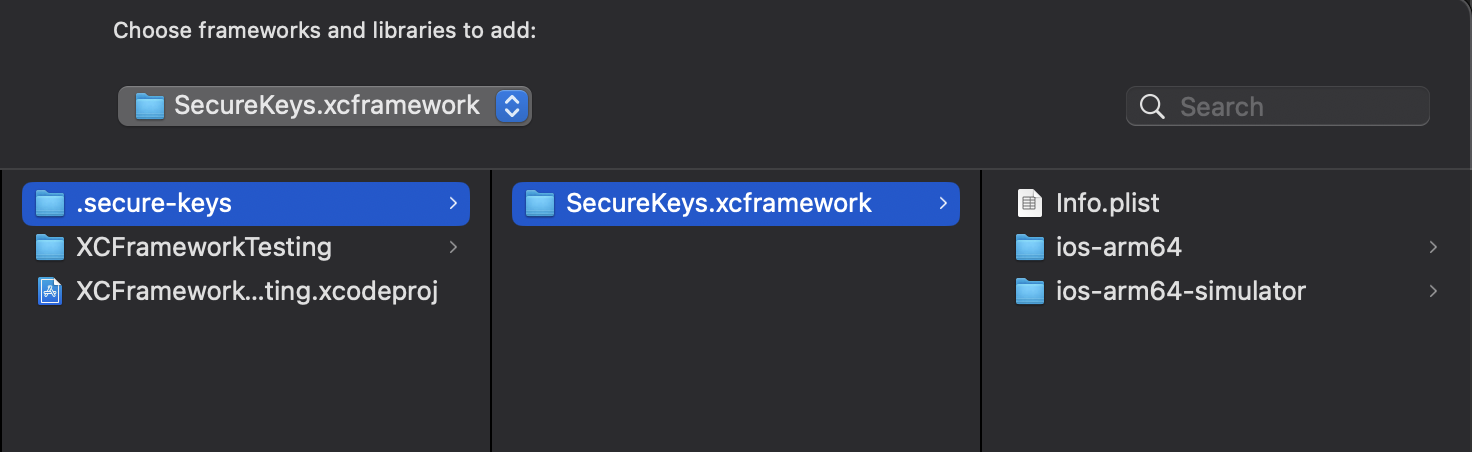
- Navigate to the
Securekeysdirectory and select theSecureKeys.xcframeworkfolder.
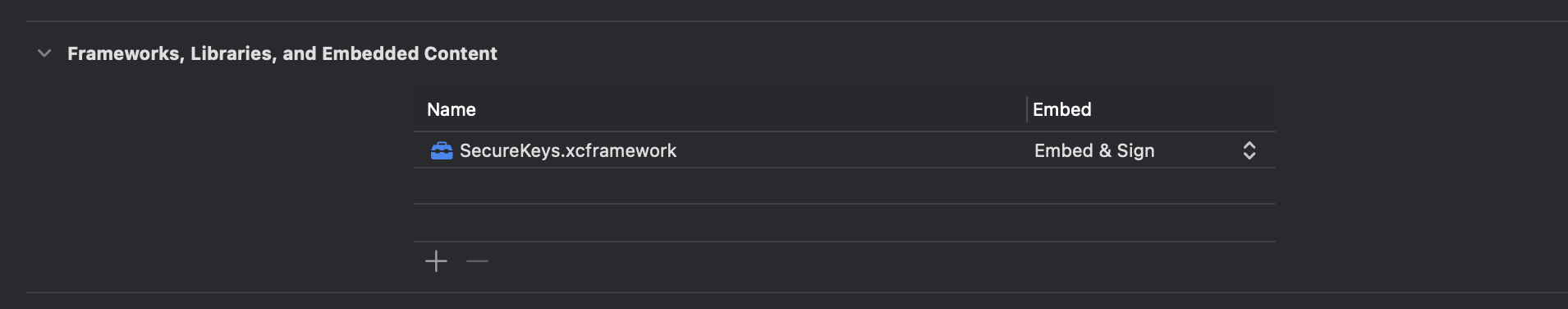
Now the
SecureKeys.xcframeworkis added to the iOS project.
- Click on the
Build settingstab and search for theSearch Pathssection.
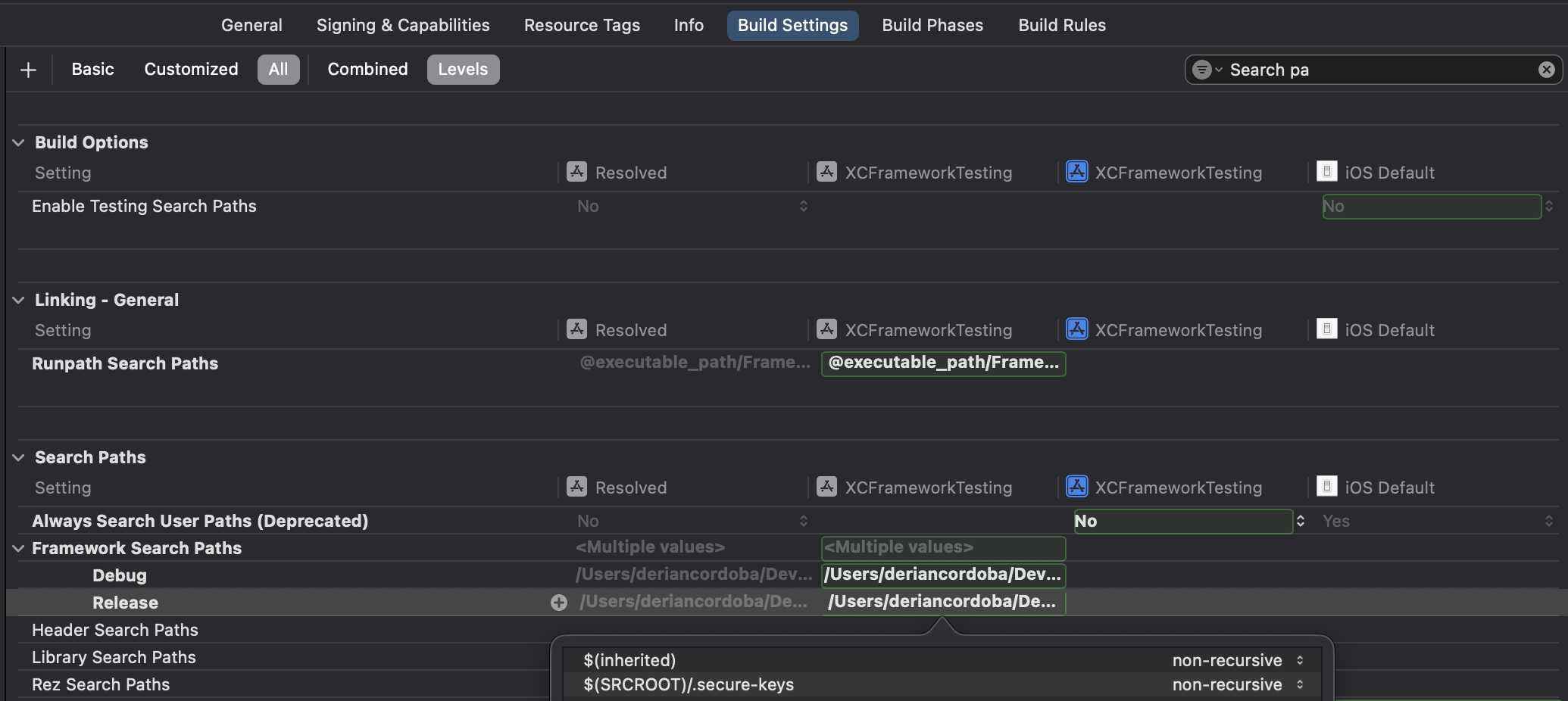
Add the path to the
SecureKeys.xcframeworkin theFramework Search Pathssection.
$(inherited)
$(SRCROOT)/.secure-keys
Step 4: Use the Keys in Your Code
In your iOS code, you can now use the Keys framework to securely retrieve your keys:
import SecureKeys
// Using the key directly
let apiKey = SecureKey.apiKey.decryptedValue
// Accessing a key by enum case
let someKey: String = key(for: .someKey)
// Another way to access the key
let someKey: String = key(.someKey)
// Using the raw value to access the key
let apiKey: SecureKey = "apiKey".secretKey
// Accessing decrypted value from the raw key
let apiKey: String = "apiKey".secretKey.decryptedValue
// Using the `key` method to retrieve the key
let apiKey: String = .key(for: .apiKey)
How It Works
When the script is executed, it follows these steps:
- A
.secure-keysdirectory is created. - A temporary Swift Package is generated within the
.secure-keysdirectory. - The Keys source code is copied into the temporary Swift Package.
- The
SecureKeys.xcframeworkis generated using the temporary Swift Package. - The temporary Swift Package is removed.
public enum SecureKey {
// MARK: - Cases
case apiKey
case someKey
case unknown
// MARK: - Properties
/// The decrypted value of the key
public var decryptedValue: String {
switch self {
case .apiKey: [1, 2, 4].decrypt(key: [248, 53, 26], iv: [148, 55, 47], tag: [119, 81])
case .someKey: [1, 2, 4].decrypt(key: [248, 53, 26], iv: [148, 55, 47], tag: [119, 81])
case .unknown: fatalError("Unknown key \(rawValue)")
}
}
}
License
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the License file for more information.